Diagnosis Means
2D Radiography
More common method of detection.
Accompanied by genetic testing.
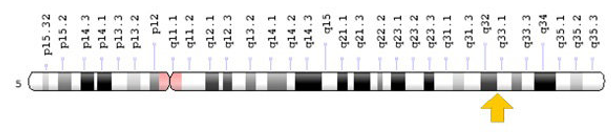
2D sonography show less details of the fetal features. The mandible angle and inferior facial angle indicated hypoplastic angle.
More common method of detection.
Accompanied by genetic testing.
2D sonography show less details of the fetal features. The mandible angle and inferior facial angle indicated hypoplastic angle.
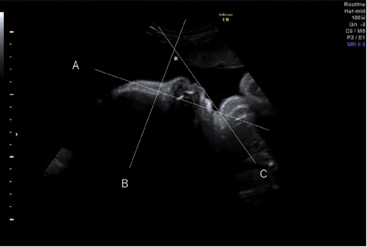
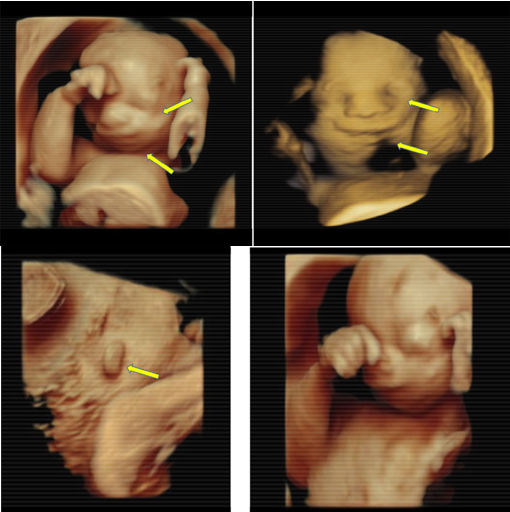
3D/4D imaging show fetal features that aid in the differential diagnosis of TCS. Unlike 2D imaging, 3D/4D can show micrognathia,palpebral downslanting, macrostomia, and microtia
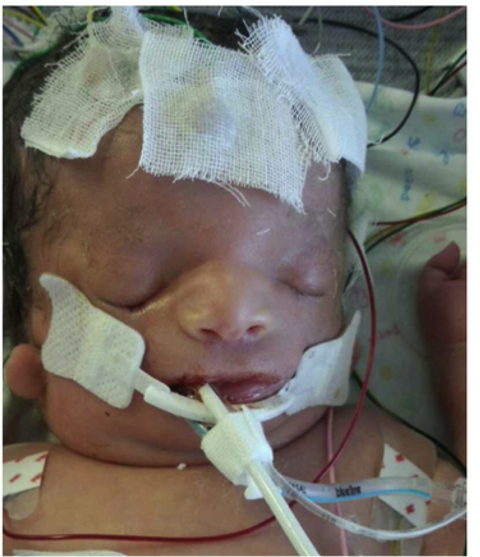
| Airway | Feeding & Dental | Speech & Hearing | Ocular |
|---|---|---|---|
Obstruction to airway tract detected by:
|
Could display palate clefts |
- External auditory canal &middle ear are often stenoic =>
monitored for development of cholesteotomas.
- Progression of obstructive sleep apnea |
Down-slanting palpebral fissuers are seen |
As the patient grows older, ongoing monitoring of their case is needed to assess their development and the implications of the syndrome. In addition, several treatment procedure are undertaken. click on the text below ...
Mandible Assessment: Palpation over TMJ and muscles of mastication to detect noises during centric and eccentric movements. Jaw Functional Scale (JFS) is a set of questions that help assess jaw functions in people with TMJ disorders.
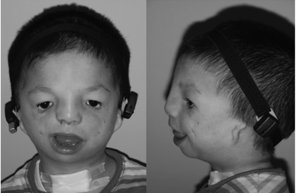 Diagnostic source 3
Diagnostic source 3
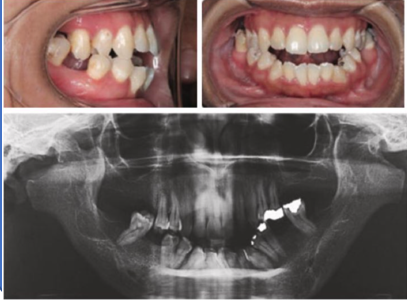 Clinical features source 1
Clinical features source 1