Radiographical Records
Radiographical findings can be interpreted by:
- Computer tomography (CT scan)
- Orthopantomogram
- Occipital X-ray photograph
| Structural deformity | Treacher-Collins syndrome | Normal |
|---|---|---|
| Zygomatic hypoplasia |
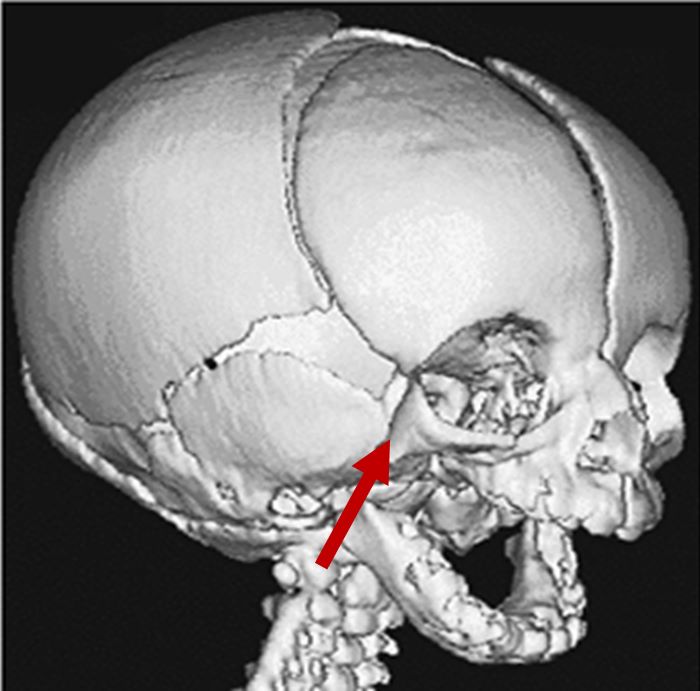
3D CT scan showing missing zygomatic arch Radiographical features source 4 |
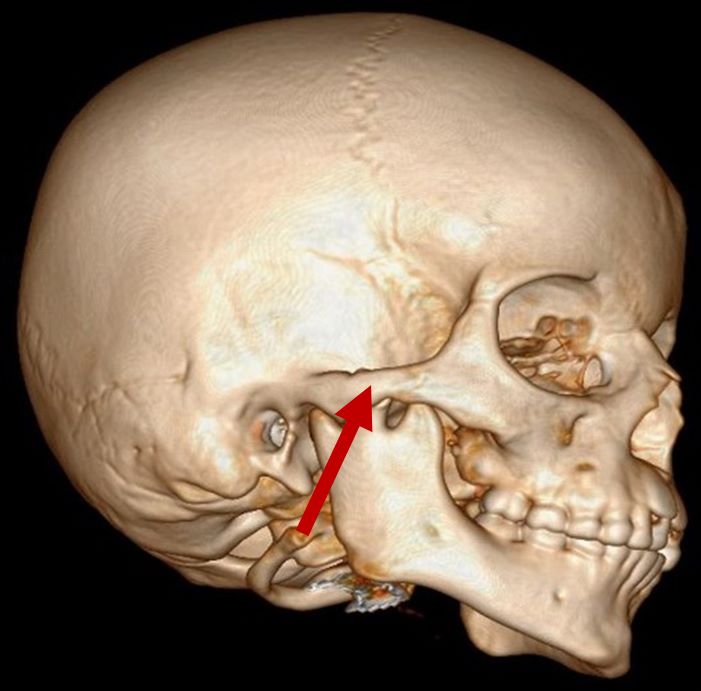
3D CT scan showing normal zygomatic arch Radiographical features source 8 |
| Airway obstruction |
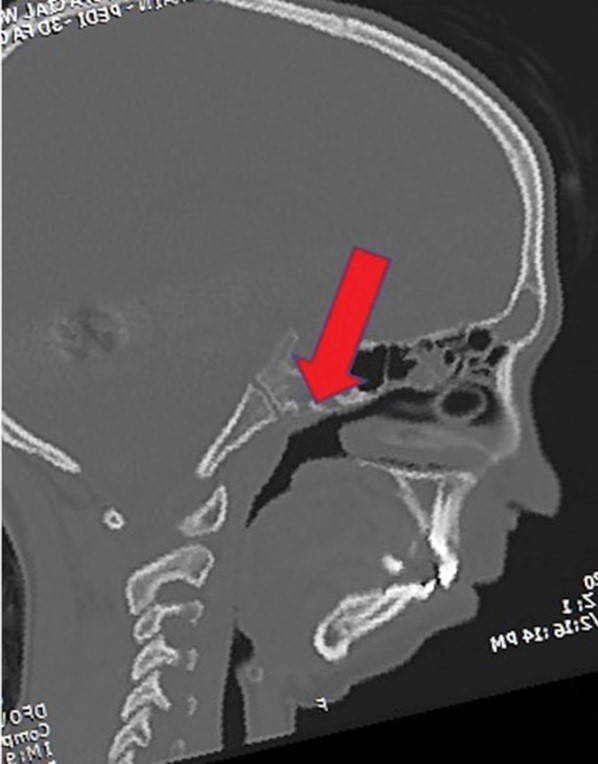
2D CT scan showing blocked airway Radiographical features source 7 |
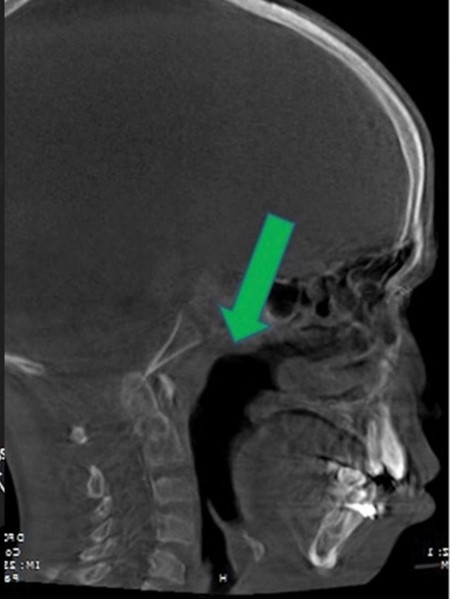
2D CT scan showing normal open airway Radiographical features source 7 |
| Middle ear deformities |
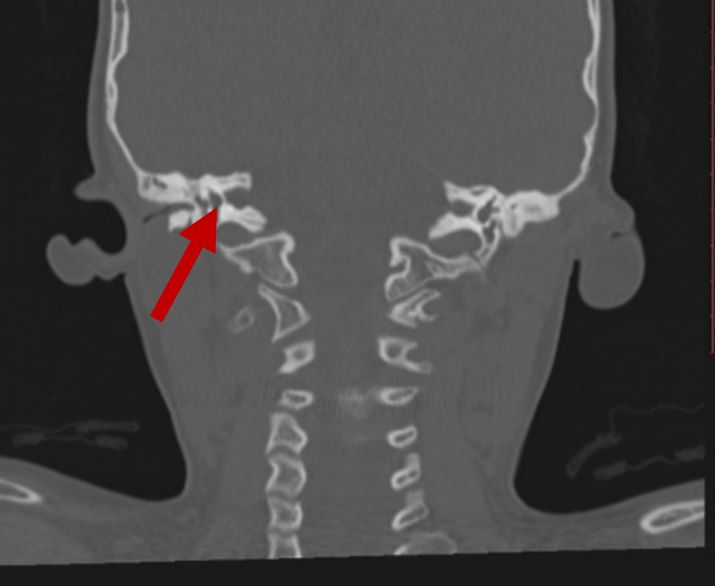
2D CT scan showing deformed middle ear structure Radiographical features source 8 |
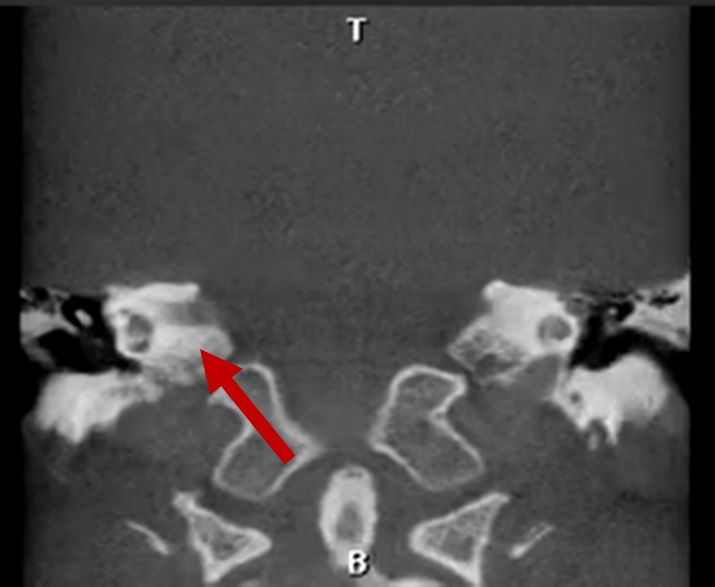
2D CT scan showing normal middle ear structure |
| No auditory ossicles |
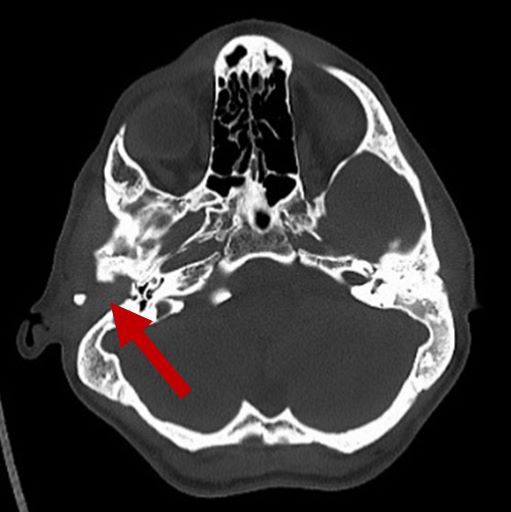
2D CT scan showing missing auditory ossicles Radiographical features source 7 |
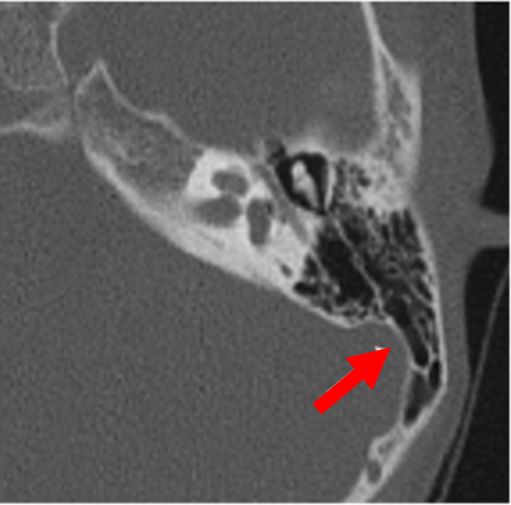
2D CT scan showing normal auditory ossicles Radiographical features source 7 |
| Mandibular hypoplasia |
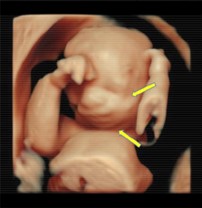
Prenatal 3D\4D ultrasound showing underdeveloped mandible Radiographical features source 2 |
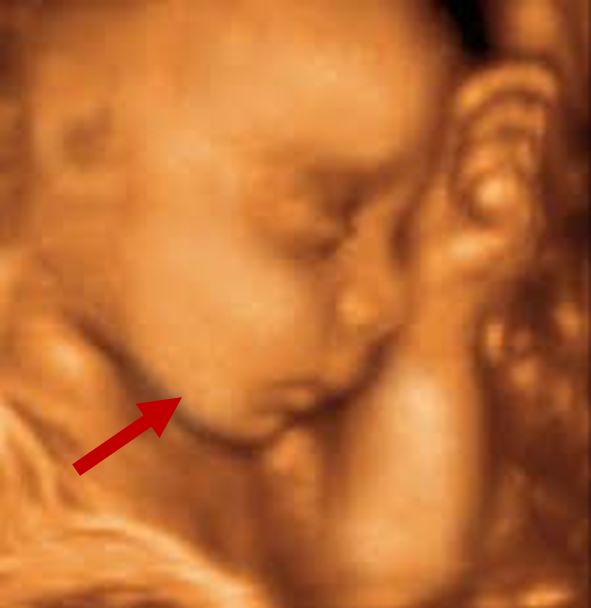
Prenatal 3D\4D ultrasound showing normal development of the mandible Radiographical features source 2 |
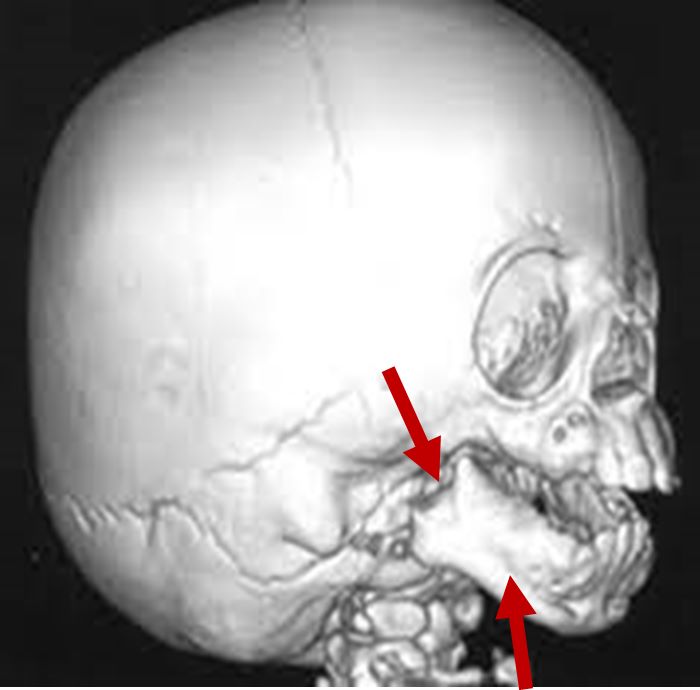
3D CT scan showing underdeveloped ramus and mandible Radiographical features source 8 |
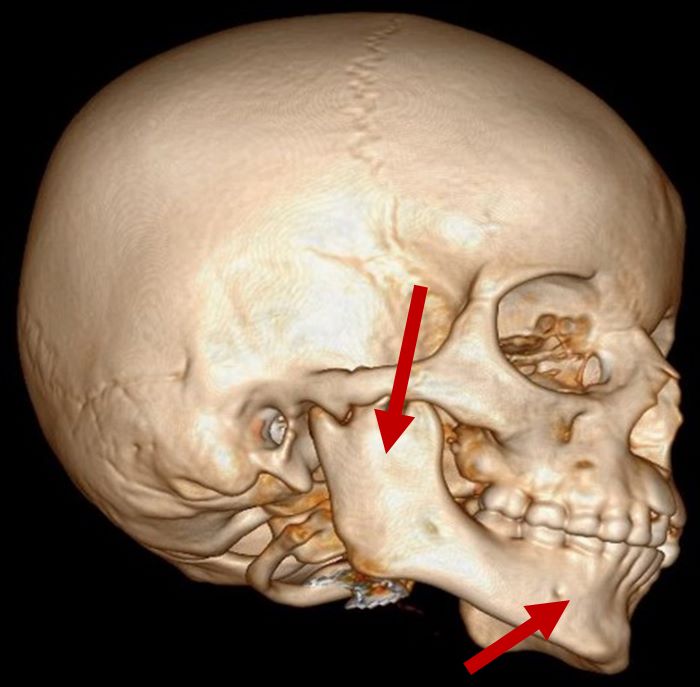
3D CT scan showing normal mandibular and ramus development Radiographical features source 8 |
|
| Fused vertebrae |
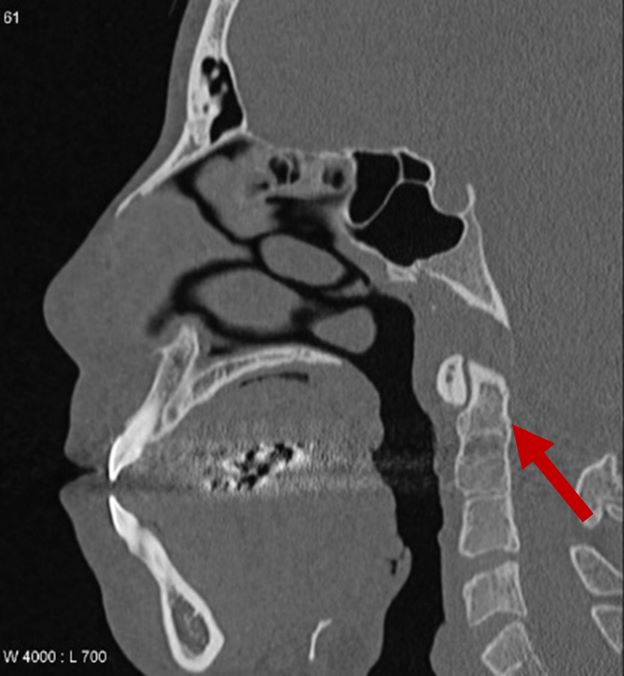
2D CT scan showing fused 2nd and 3rd vertebrae Radiographical features source 9 |
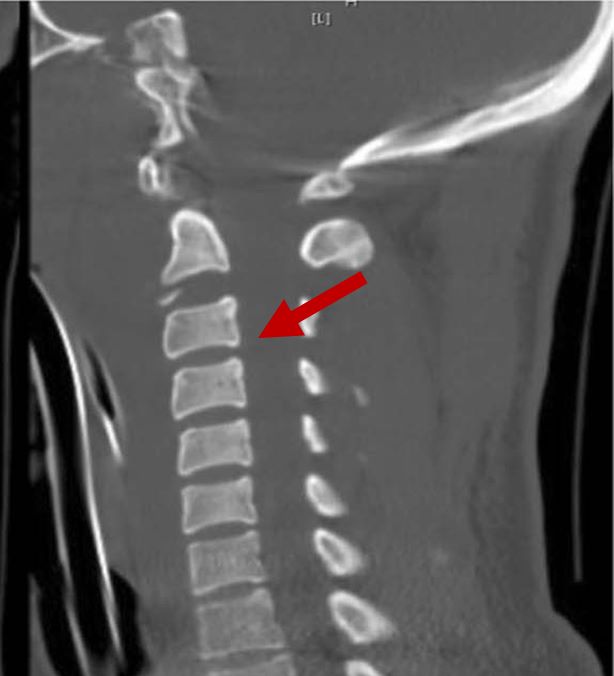
2D CT scan showing normal vertebrae Radiographical features source 6 |
| The findings between cases are typically similar with some difference in the severity. | ||